Resource PKI (RPKI)Japanese Page
Last updated: November 13, 2024
Published: February 25, 2015
What is Resource PKI (RPKI)?
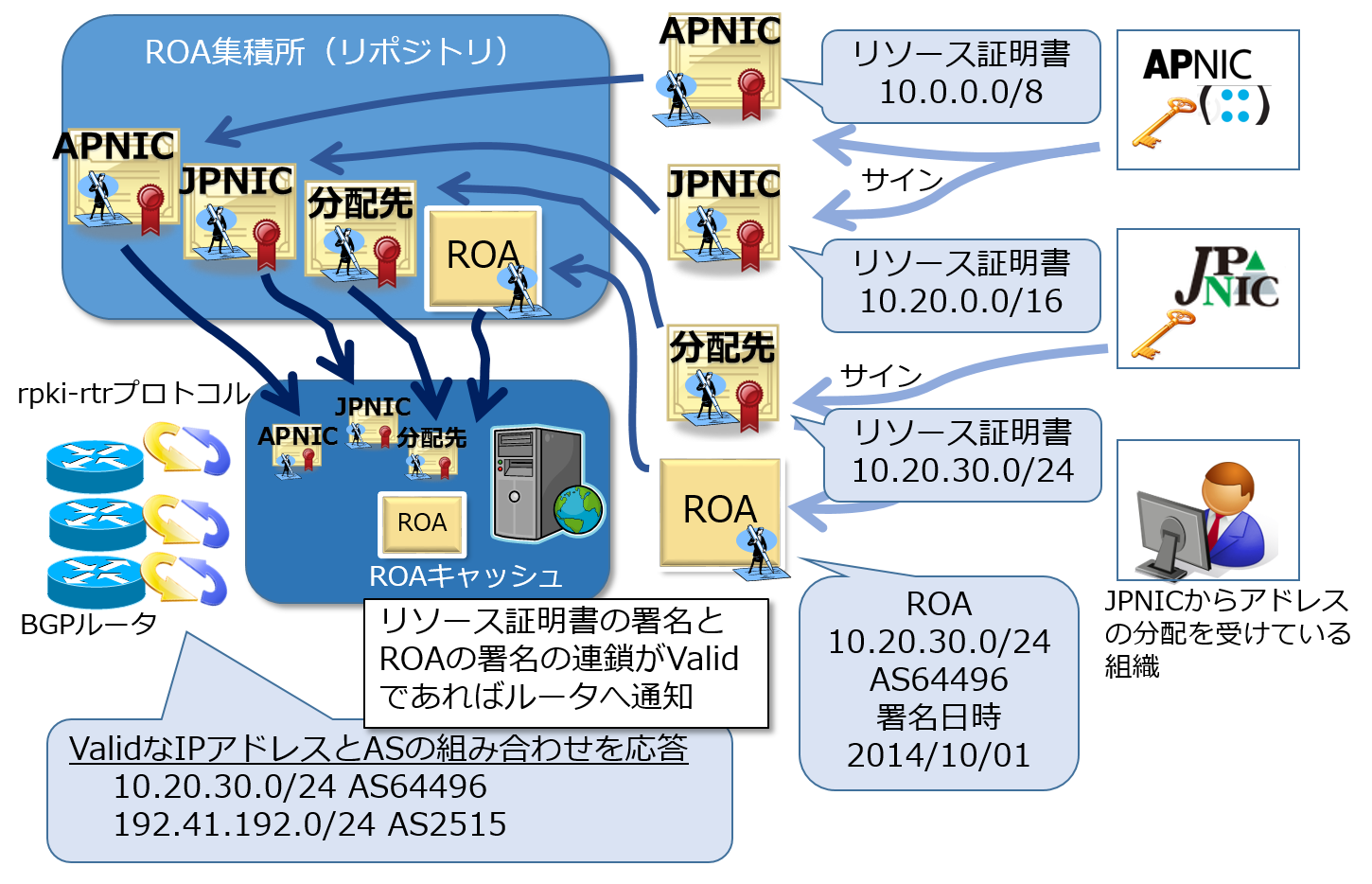
Resource PKI (RPKI) is a Public-Key Infrastructure (PKI) for proving the allocation and assignment of Internet number resources. It enables verification of whether IP addresses have been properly allocated, and can be used to detect incorrect Internet routing information (Mis-Origination) in BGP routers. Digital certificates called Resource Certificates, which prove the allocation and assignment of IP addresses, are issued using RPKI.
In Internet routing using BGP, “IP addresses” and “Autonomous System Numbers (AS numbers), which identify networks on the Internet,” are exchanged. Resource Certificates can be used to generate data called “Route Origin Authorization (ROA),” which indicates the correct combination of IP addresses and AS numbers.
By using these ROAs, BGP routers can verify whether the origin (the AS that generates routing information for a particular IP address block) matches the authorized holder of the IP address. This mechanism is called Route Origin Validation (ROV) or Origin Validation. Since BGP itself does not have a mechanism for validating the authenticity of routing announcements, routing information collected may include both correct and incorrect routes, often due to operator mistakes or misconfigurations. Introducing ROV into BGP routing allows routers to validate whether the combination of IP addresses and AS numbers is correct, based on ROAs.
For more details, please see the JPNIC blog: “What is RPKI? - Its Origin and the Present”.
- What is Resource PKI? (1-Minute Internet Terminology)
- What is ROA? (1-Minute Internet Terminology)
- What is ROV? (1-Minute Internet Terminology)
- Incorrect Internet Routing Information (Mis-Origination) in BGP Routers
Guidelines for Countermeasures Against Invalid Routes on the Internet Using RPKI ROAs
These guidelines are intended for executives and engineers of domestic ISPs and other organizations involved in the connectivity and technical operations of the Internet. They provide guidance for countermeasures against invalid routing information on the Internet, particularly measures using RPKI. The document presents considerations that can help organizations and individuals decide whether to adopt RPKI-based countermeasures to mitigate various problems caused by invalid routing information and to deter malicious use of such information in cybercrime.
RPKI Systems Provided by JPNIC
RPKI System

The JPNIC RPKI system issues Resource Certificates based on the IP address and AS number database. It is linked with the APNIC RPKI system, and Resource Certificates are issued according to IP address and AS number allocations. These issued Resource Certificates can then be used to generate ROAs (Route Origin Authorizations).
|
Registration Method (How to Create and Manage ROAs) |
How to Access JPNIC ROA Web (for those who have received IP address allocations) | |
|---|---|---|
Available Functions
|
||
Requirements
|
||
| How to Connect to the RPKI System via BPKI (for those who have received IP address allocations) | ||
Available Functions
|
||
Requirements
|
||
|
Downloading ROAs / Checking Routing Information |
How to Use via ROA Cache (available to anyone) | |
| You can use the Resource Certificates and ROAs issued by the RPKI system. For more details, see “How to Set Up an ROA Cache Server”. | ||
RPKI Testbed
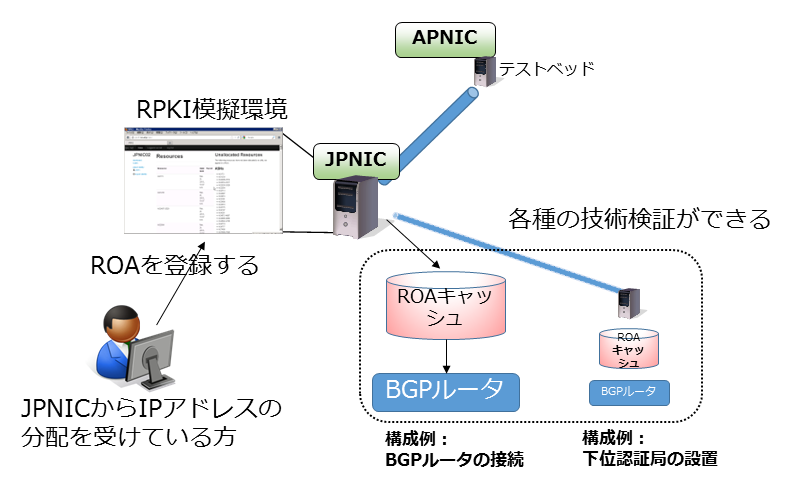
JPNIC provides an RPKI testbed as an environment where RPKI can be easily tried. The testbed allows users to experience the use of RPKI and is linked with the APNIC RPKI test environment (APNIC Testbed).
To make full use of RPKI, the IP addresses contained in Resource Certificates should be based on the IP registry system database. Since the testbed is intended for RPKI experimentation and technical validation, JPNIC staff input IP address allocation information according to the wishes and needs of testbed users. Users can issue ROAs via the web interface. ROAs issued in the testbed are transferred through several processes to the ROA Public Cache Server, enabling verification on BGP routers.
The RPKI testbed can be used to verify technical operations such as issuing ROAs through the web interface by users who have received IP address allocations, and processing those ROAs with ROA caches deployed by the users themselves.
It is also possible to configure RPKI software (e.g., RPKI Tools) capable of issuing Resource Certificates within your organization, connect it to the JPNIC testbed, and perform operational verification.
If you wish to use the RPKI testbed, please contact the JPNIC RPKI team at <rpki-query@nic.ad.jp>.
ROA Public Cache Server
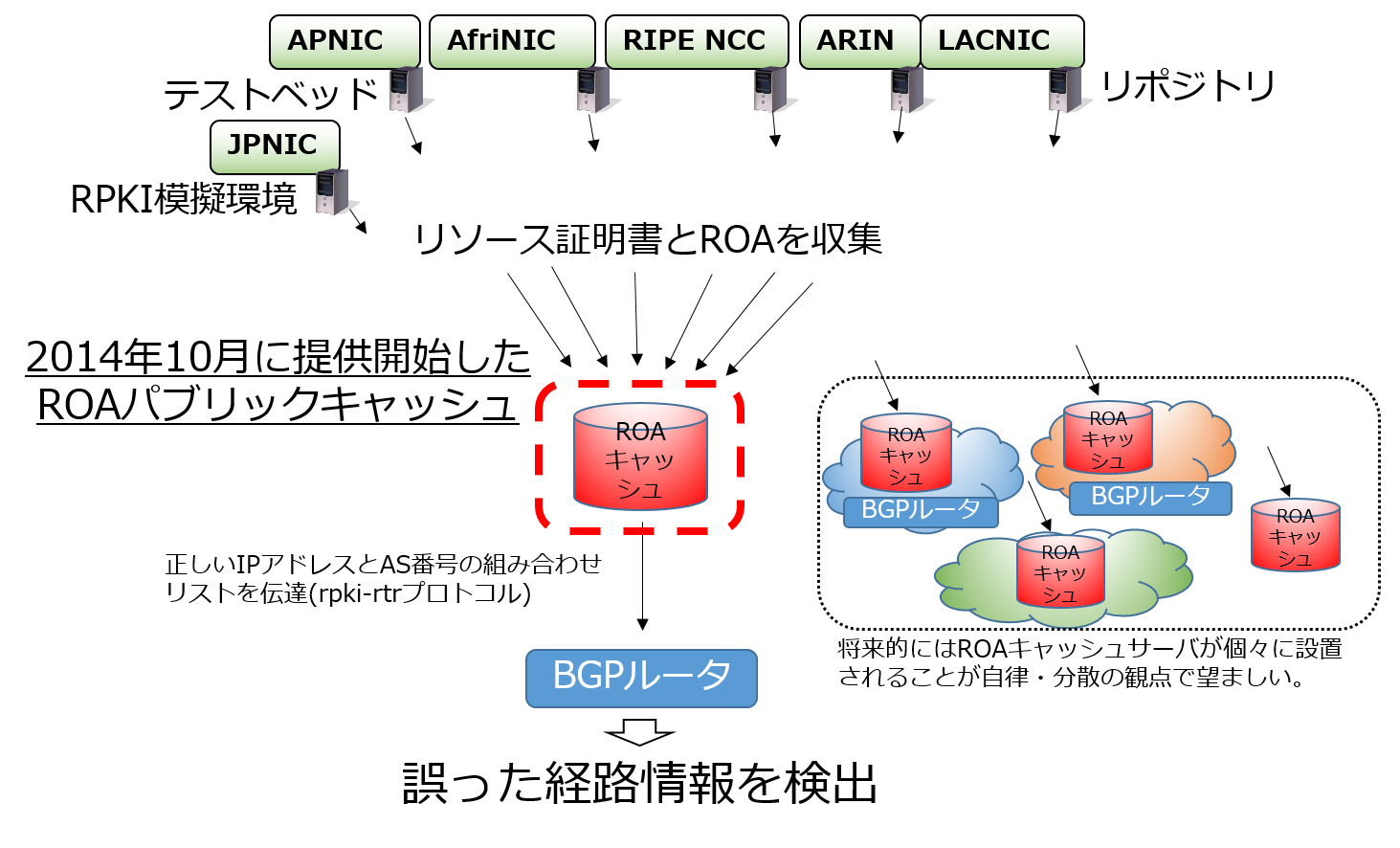
An ROA cache server collects Resource Certificates and ROAs and verifies their digital signatures. As a result of verification, a “list of valid IP address and AS number combinations” is generated. BGP routers receive this list from the ROA cache server using the rpki-rtr protocol and compare it before inserting routes into the routing table. This mechanism is called Origin Validation.
The JPNIC ROA Public Cache Server collects ROAs issued internationally as well as those issued in the JPNIC RPKI testbed. The JPNIC-provided public cache server is a “shared” RPKI cache server referred to by individual BGP routers. However, it is ideal for each network to operate its own ROA cache server individually.
When BGP routers compare ROAs with routing information, routes are classified into three categories: Valid (ROA matches the route), Invalid (ROA does not match the route), and Not Found (no matching ROA exists for the route). This makes it possible to detect incorrect routing information. Depending on the classification, operators can prefer valid routes, de-preference invalid ones, or ignore them (exclude them from the routing table).
For information on how to use the ROA Public Cache Server, see the following:
In addition to using the ROA Public Cache Server, you can also deploy your own ROA cache server. For more details, see the following:
Introductory Video on RPKI Basics
Related Links
| Japan | MF RPKI Project | The ROA cache server and RPKI page of Internet Multifeed Co. |
|---|---|---|
| RPKI Implementations | RPKI Tools | Open-source software implementing RPKI CAs and signature verification programs. |
| BGP Secure Routing Extension (BGP-SRx) | An RPKI implementation for the Quagga routing software. | |
| RPSTIR | An RPKI signature verification program. | |
| RTRlib | A C language implementation of an RPKI signature verification program. | |
| Tools and Resources | This page provides the RPKI Validator signature verification program and sample router configurations. | |
| RPKI Dashboard | A website where you can view the issuance status of Resource Certificates and ROAs in the five RIRs and comparison results with routing information. | |
| RIR | Web pages on RPKI at each RIR. | |
| RPKI Standardization | IETF sidrops WG | The development of specifications related to RPKI is being carried out here. |
| Others | Keiro-chan Newsletter Volume.1 (193KB) | A local newsletter connecting people interested in RPKI and JPNIC. |




